Welcome to our comprehensive guide on dental implants, where we delve into the intricate details of how Dental Implants work. replacements work. Dental implants have revolutionized the field of dentistry, offering a reliable and long-lasting solution for those missing one or more teeth. In this guide, we’ll explore the anatomy of dental implants, the process of osseointegration, the placement procedure, and the various types available. We’ll also discuss the numerous benefits they offer, such as improved oral health, functionality, and aesthetics.
Definition of Dental Implants
Dental implants are prosthetic devices surgically implanted into the jawbone to replace missing teeth. They serve as artificial tooth roots, providing a stable foundation for dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, or dentures. Made of biocompatible materials like titanium, dental implants fuse with the surrounding bone through a process called osseointegration, ensuring durability and stability.
Anatomy of Dental Implants
Components of Dental Implants
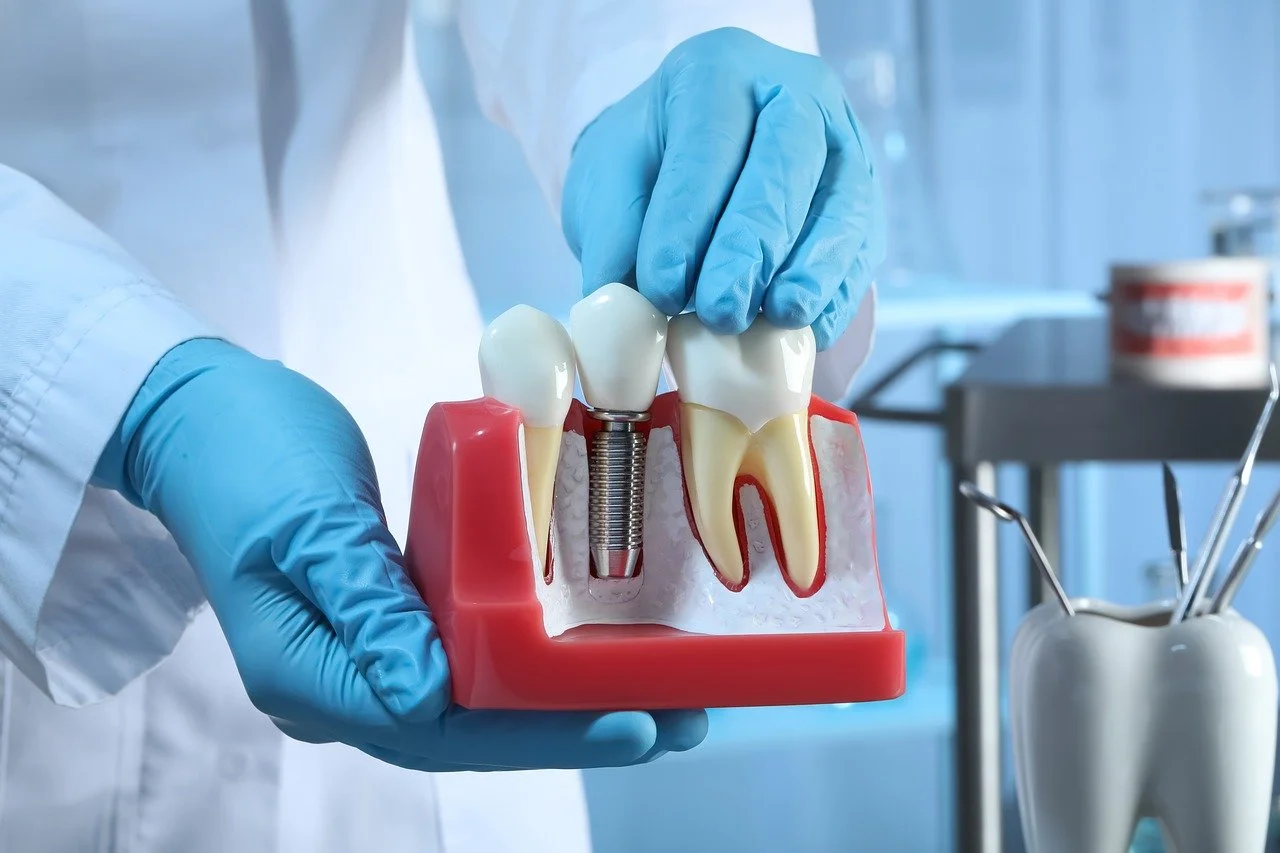
- Implant Fixture: This is the part of the implant that is surgically placed into the jawbone. Typically made of titanium, the implant fixture resembles a small screw and serves as the artificial tooth root.
- Abutment: The abutment is a connector piece that attaches to the implant fixture. It protrudes above the gum line and provides support for the dental restoration. Abutments can be prefabricated or custom-made based on the patient’s specific needs.
- Prosthetic Crown or Restoration: The prosthetic crown or restoration is the visible part of the dental implant that resembles a natural tooth. It is typically made of porcelain or ceramic and is custom-designed to match the shape, size, and color of the patient’s existing teeth.
Role of Each Component
- Implant Fixture: The implant fixture acts as the foundation for the dental implant, anchoring it securely within the jawbone. Through osseointegration, the implant fixture integrates with the surrounding bone tissue, providing stability and support.
- Abutment: The abutment serves as a connector between the implant fixture and the prosthetic crown or restoration. It ensures a secure attachment and allows for adjustments to achieve proper alignment and aesthetics.
- Prosthetic Crown or Restoration: The prosthetic crown or restoration is the functional and aesthetic component of the dental implant. It mimics the appearance and function of a natural tooth, allowing patients to bite, chew, and speak comfortably. Additionally, it restores the patient’s smile, improving confidence and overall oral health.
How Dental Implants Work
Understanding the process of How Dental Implants work is crucial before starting the Dental Implants Treatment.
Explanation of Osseointegration
Osseointegration is a crucial process in dental implantology where the implant fixture fuses with the surrounding bone tissue. Initially introduced by Professor Per-Ingvar Brånemark in the 1950s, osseointegration revolutionized the field of dentistry by providing a reliable method for replacing missing teeth. During osseointegration, the implant fixture, typically made of titanium, is surgically placed into the jawbone. Over time, the bone cells grow and adhere to the implant’s surface, forming a strong and stable bond.
Importance of Osseointegration
Osseointegration plays a vital role in the success and longevity of dental implants. Without proper osseointegration, the dental implant may fail to integrate with the surrounding bone tissue, leading to implant instability, discomfort, and ultimately, implant failure. The process ensures that the implant becomes a functional part of the jawbone, providing the necessary support for dental prosthetics such as crowns, bridges, or dentures. Osseointegration helps distribute chewing forces evenly across the implant and surrounding bone, preventing bone loss and maintaining the structural integrity of the jaw.
Achieving successful osseointegration requires careful treatment planning, precise surgical techniques, and adherence to post-operative care instructions. Factors such as patient’s overall health, bone quality and quantity, implant design, and surgical technique influence the osseointegration process. Certain systemic conditions such as diabetes or smoking can negatively impact osseointegration, highlighting the importance of thorough patient evaluation and risk assessment before proceeding with dental implant treatment.
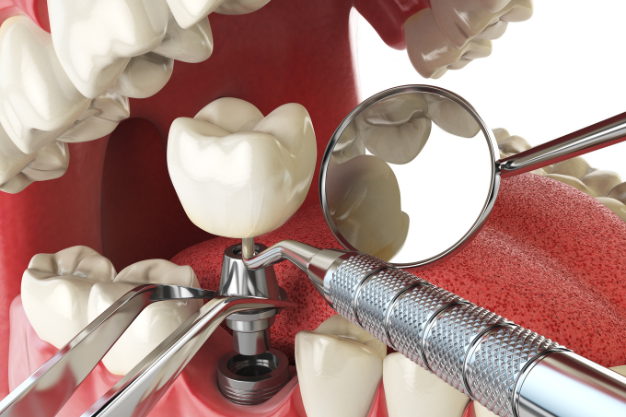
Placement Procedure
Dental Implant Procedure
The placement procedure for dental implants involves several stages, starting with a comprehensive examination and treatment planning. During the initial consultation, the dental professional evaluates the patient’s oral health, including the condition of the jawbone and surrounding tissues, and discusses treatment options. Once the treatment plan is finalized, the actual implant placement procedure begins.
The implant placement procedure typically consists of several steps. First, the surgical site is numbed using local anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort during the procedure. Then, an incision is made in the gum tissue to expose the underlying jawbone. Using specialized instruments, the dentist prepares the bone tissue to receive the implant fixture. The implant fixture, usually made of biocompatible titanium, is then carefully placed into the jawbone at the predetermined location.
After the implant is positioned, the gum tissue is sutured back into place, and a healing cap or cover screw may be placed over the implant to protect it during the initial healing period. In some cases, the implant may be left to heal and integrate with the surrounding bone tissue before proceeding with the next stage of treatment.
Role of Dental Professionals
Dental professionals play a crucial role in every step of the dental implant placement procedure. From the initial consultation to the post-operative care, their expertise and skill ensure the success and longevity of the dental implant treatment. Dentists, oral surgeons, and periodontists are the primary professionals involved in dental implant placement.
During the treatment planning phase, the dental professional assesses the patient’s oral health, evaluates the suitability of dental implants, and develops a customized treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs and preferences. Throughout the procedure, the dental professional performs the surgical placement of the implant fixture with precision and accuracy, taking into account factors such as bone density, anatomy, and esthetics.
Following the implant placement, dental professionals monitor the patient’s healing progress and provide instructions for post-operative care to promote optimal healing and osseointegration. They also oversee the restoration phase, where prosthetic components such as crowns, bridges, or dentures are attached to the implants to restore function and aesthetics.
Types of Dental Implants
There are several types of dental implants available, each designed to address specific dental needs and anatomical considerations. To understand how dental implants work, its essential to know about the different types of dental implants.
Different Types of Dental Implants
- Endosteal Implants: Endosteal implants are the most common type of dental implant and are surgically placed directly into the jawbone. These implants resemble small screws or cylinders and provide a stable foundation for artificial teeth.
- Subperiosteal Implants: Subperiosteal implants are placed under the gum tissue but above the jawbone. They are typically used when the patient lacks sufficient jawbone density to support traditional implants. Subperiosteal implants consist of a metal frame that sits on the jawbone and prosthetic teeth attached to the frame.
- Zygomatic Implants: Zygomatic implants are longer than traditional implants and are anchored in the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) rather than the jawbone. They are used in cases where patients have insufficient jawbone volume for standard implants, offering an alternative solution for implant-supported restorations.
- All-on-4 Implants: All-on-4 implants, also known as full-arch implants, are designed to replace an entire arch of teeth using just four implants. This innovative approach allows for the efficient restoration of a full set of teeth with minimal surgery and recovery time.
- Mini Dental Implants: Mini dental implants are smaller in diameter than traditional implants and are often used to stabilize removable dentures or support single-tooth restorations in areas with limited space or bone volume.
Selecting the Most Suitable Type of Dental Implant
Choosing the right type of dental implant requires careful consideration of various factors, including the patient’s oral health, jawbone structure, aesthetic preferences, and budgetary constraints.
- Consultation with a Dental Professional: Before undergoing dental implant treatment, patients should schedule a consultation with a qualified dental professional. During this appointment, the dentist will assess the patient’s oral health and discuss treatment options based on their individual needs and goals.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays and CT scans, may be necessary to evaluate the quantity and quality of the jawbone and identify any underlying dental issues that could affect the success of implant treatment.
- Customized Treatment Plan: Based on the patient’s oral health status and treatment objectives, the dental professional will develop a customized treatment plan outlining the type of dental implant best suited to their needs. Factors such as implant location, size, and material will be carefully considered to ensure optimal outcomes.
- Patient Education: Patients need to understand the benefits and limitations of each type of dental implant, as well as the anticipated treatment timeline, potential risks, and expected results. Open communication with the dental team is crucial for making informed decisions about implant treatment.
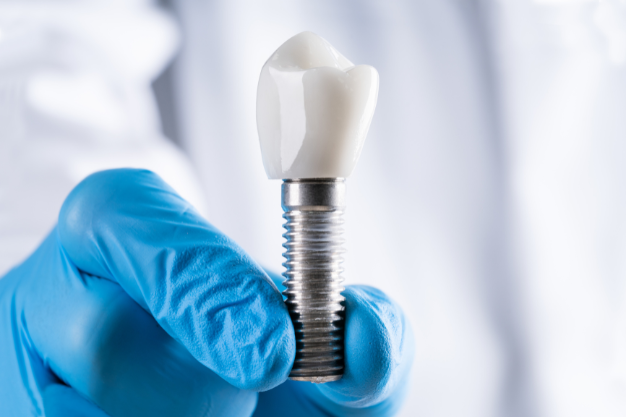

Benefits of Dental Implants
Dental implants are a popular and effective solution for replacing missing teeth and restoring oral function and aesthetics. These innovative dental prosthetics offer numerous benefits over traditional tooth replacement options, making them an attractive choice for patients seeking a long-term solution to tooth loss.
Advantages of Dental Implants Over Traditional Tooth Replacement
Dental implants offer several advantages compared to traditional tooth replacement options such as bridges or dentures. Unlike bridges, which require adjacent teeth to be shaved down for support, dental implants do not rely on neighboring teeth for stability. This preserves the integrity of surrounding teeth and reduces the risk of damage or decay. Additionally, dental implants provide a more permanent solution to tooth loss than removable dentures, which can shift or become loose over time.
Impact on Oral Health, Function, and Aesthetics
One of the primary benefits of dental implants is their ability to restore oral function and aesthetics. Implants closely mimic the appearance and function of natural teeth, allowing patients to eat, speak, and smile with confidence. Unlike dentures, which can impair speech and limit dietary choices, dental implants provide a stable and comfortable chewing surface that closely resembles natural teeth. This improves overall quality of life and enhances self-esteem.
Furthermore, dental implants help preserve oral health by stimulating the jawbone and preventing bone loss. When a tooth is lost, the underlying jawbone can begin to deteriorate over time due to lack of stimulation. Dental implants act as artificial tooth roots, stimulating the surrounding bone tissue and preventing bone resorption. This helps maintain facial structure and prevent changes in facial appearance associated with tooth loss.
Conclusion
Dental implants offer a revolutionary solution for individuals suffering from tooth loss, providing numerous benefits over traditional tooth replacement options. With their ability to restore oral function, aesthetics, and overall quality of life, dental implants have become the gold standard in modern dentistry. By closely mimicking the appearance and function of natural teeth, implants offer patients a long-lasting and reliable solution that enhances both oral health and self-confidence. The preservation of jawbone structure and prevention of bone loss contribute to the long-term success of dental implant treatment. Overall, dental implants represent a valuable investment in oral health and well-being, offering patients a permanent solution to tooth loss that significantly improves their quality of life.
FAQs
Are dental implants suitable for everyone?
Dental implants are suitable for most individuals who are in good overall health and have sufficient jawbone density to support the implants. However, a thorough evaluation by a qualified dental professional is necessary to determine candidacy for implant treatment.
How long do dental implants last?
With proper care and maintenance, dental implants can last a lifetime. However, the longevity of implants depends on various factors such as oral hygiene practices, lifestyle habits, and overall health.
Is the dental implant procedure painful?
The dental implant procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, ensuring that patients experience minimal discomfort during the process.