Composite bonding is a popular dental procedure that involves the application of a tooth-colored composite material to enhance the appearance and functionality of teeth. This non-invasive and versatile technique has gained significant importance in dentistry, providing effective solutions for various dental issues. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of how does composite bonding work, highlighting its benefits and considerations.
Definition of Composite Bonding
Composite bonding refers to the process of applying a dental composite material to the teeth. The composite material, which is a mixture of resin and finely ground glass particles, is carefully matched to the natural color of the patient’s teeth, resulting in a seamless and natural-looking restoration for teeth. This technique is commonly used to repair chipped or cracked teeth, close gaps, reshape teeth, and improve overall smile aesthetics.
Importance of Composite Bonding in Dentistry
Composite bonding plays a crucial role in modern dentistry for several reasons:
Aesthetic Enhancement
Composite bonding offers exceptional aesthetic results, allowing individuals to achieve a beautiful smile. The composite material can be precisely shaped and shaded to match the surrounding teeth, providing a seamless and natural appearance. It addresses cosmetic concerns such as tooth discoloration, uneven tooth shapes, and minor misalignments, enhancing patients’ self-confidence and self-esteem.
Preservation of Natural Tooth Structure
Unlike certain dental procedures that require significant tooth reduction, composite bonding preserves the natural tooth structure. The process involves minimal removal of the tooth enamel, ensuring that healthy tooth substance is conserved. This conservative approach is advantageous as it maintains the long-term health and strength of the teeth.
Non-Invasive Procedure
Composite bonding is a non-invasive procedure that typically does not require anesthesia. Unlike more invasive treatments like dental crowns or veneers, which involve extensive tooth preparation, composite bonding is relatively quick and straightforward. Patients can enjoy the benefits of a transformed smile without undergoing complex and time-consuming procedures.
Versatility in Addressing Dental Issues
Composite bonding is a versatile technique that can address various dental concerns. It can effectively repair small chips or fractures, close gaps between teeth, lengthen worn teeth, and reshape irregular or misshapen teeth. Additionally, composite bonding can be used in combination with other cosmetic or restorative treatments, such as teeth whitening, to achieve comprehensive smile makeovers.
Understanding Composite Bonding
Composition of Dental Composite Material
Composite materials used in bonding procedures consist of a mixture of resin and finely ground glass particles. This combination provides both strength and aesthetics. The resin component is typically made of a dental-grade composite material, which is color-matched to the patient’s teeth. The glass particles, often referred to as fillers, enhance the material’s durability and mimic the translucency of natural tooth enamel.
The composite material’s composition allows it to be molded and shaped to create a natural-looking restoration. It is also resistant to staining and wear, ensuring longevity and maintaining the desirable aesthetic outcome.
Role of Dental Adhesives
Dental adhesives play a crucial role in the success of composite bonding procedures. These adhesives, also known as bonding agents, facilitate the adhesion of the composite material to the tooth structure. They create a strong bond between the tooth enamel or dentin and the composite material, ensuring a durable and long-lasting restoration.
The dental adhesive is applied after the tooth surface has been prepared, creating a micromechanical bond between the composite material and the tooth structure. This bond enhances the structural integrity of the bonded restoration, preventing detachment or debonding over time.
Types of Composite Bonding Procedures
Direct Composite Bonding
Direct composite bonding is the most common type of composite bonding procedure. It involves the application of the composite material directly onto the tooth surface. The dentist carefully molds and sculpts the material to achieve the desired shape and contour, ensuring seamless integration with the natural tooth structure. Once the desired shape is achieved, a curing light is used to harden the composite material, resulting in a strong and durable restoration.
Indirect Composite Bonding
In some cases, indirect composite bonding may be recommended. This involves fabricating the composite restoration outside the mouth, typically in a dental laboratory. The restoration is then bonded to the tooth using dental adhesives. Indirect composite bonding is often used for more complex cases or when extensive shaping and customization are required.
How does composite bonding work? The Process of Composite Bonding
In this section, we delve into the process of How does Composite Bonding Works. We define the key points in steps so you can easily understand the procedure of how does composite bonding works.
Step 1: Tooth Preparation
Examination and Identification of the Target Tooth
The first step in the composite bonding process is a thorough examination of the tooth that requires treatment. The dentist will assess the tooth’s condition, identifying any decay, damage, or cosmetic concerns. This examination ensures that how does composite bonding work to address the specific needs of the tooth.
Removal of Decay or Damaged Portions
If the tooth exhibits signs of decay or damage, the dentist will remove the affected portions. This may involve carefully drilling away decayed areas or removing any sharp or broken edges. The goal is to create a clean and healthy foundation for the composite material to adhere to.
Reshaping the Tooth Surface
In some cases, the tooth may require reshaping to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome. The dentist uses specialized dental instruments to gently sculpt the tooth, ensuring proper alignment, symmetry, and proportions. This step is crucial in creating a natural-looking restoration that seamlessly blends with the surrounding teeth.
Step 2: Composite Material Application
Selection of Appropriate Composite Material
To ensure optimal results, the dentist carefully selects the composite material that closely matches the color and translucency of your natural teeth. This attention to detail ensures that the bonded restoration seamlessly blends with the surrounding teeth, creating a harmonious smile.
Bonding Agent Application
Before applying the composite material, the tooth surface is treated with a dental adhesive or bonding agent. This adhesive is applied to the prepared tooth structure, creating a strong bond between the tooth and the composite material. The bonding agent improves the adhesion of the composite, enhancing the longevity and durability of the restoration.
Layering and Shaping of Composite Material
The dentist skillfully applies the composite material in layers, carefully sculpting and shaping it to achieve the desired tooth shape and contour. Each layer is precisely placed and manipulated, ensuring the restoration blends seamlessly with the neighboring teeth. This layering technique allows for a natural-looking result and mimics the nuances of natural tooth anatomy.
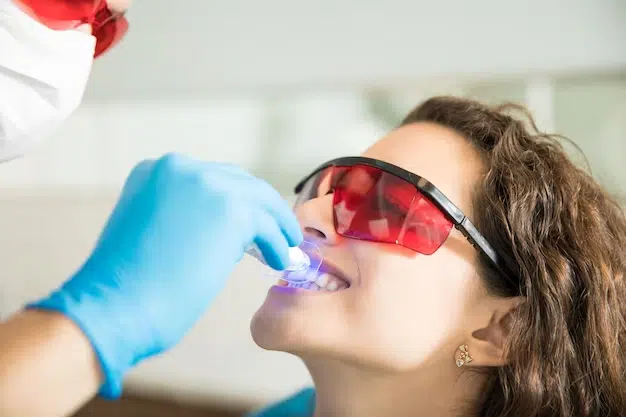
Use of Curing Light for Hardening
Once the composite material is properly shaped, a curing light is used to harden and set the material. The light emits a specific wavelength that activates the chemical reaction in the composite, causing it to harden quickly. The curing process ensures the composite becomes strong and durable, capable of withstanding normal biting and chewing forces.
Step 3: Finishing and Polishing
Trimming Excess Composite Material
After the composite material has been shaped and hardened, the dentist carefully trims any excess material. This step involves using specialized dental instruments to precisely remove any unwanted composite, ensuring that the restoration aligns seamlessly with the natural tooth structure. The dentist’s skill and expertise play a crucial role in achieving optimal contours and proportions.
Smoothing the Surface
Once the excess composite material has been removed, the dentist proceeds to smooth the surface of the restoration. This is done using fine-grit dental instruments and polishing discs. The goal is to create a smooth and polished surface that mimics the texture and luster of natural tooth enamel. The dentist pays close attention to the details, ensuring a comfortable and aesthetically pleasing result.
Polishing for a Natural Appearance
To achieve a natural and radiant appearance, the dentist performs the final polishing step. This involves using a series of polishing discs, pastes, and brushes that are specifically designed for composite materials. The dentist gently polishes the restoration, enhancing its shine and luster. The polishing process not only improves the aesthetics but also helps to reduce surface roughness, making it easier to clean and maintain the bonded restoration.
Advantages and Benefits of Composite Bonding
Aesthetic Improvement
Composite bonding offers remarkable aesthetic improvement. The composite material used in bonding procedures can be color-matched to your natural teeth, ensuring a seamless blend. This allows for the correction of various cosmetic concerns, such as chipped, discolored, or misshapen teeth. Through composite bonding, you can achieve a harmonious and radiant smile that enhances your overall facial appearance.
Conservation of Natural Tooth Structure
One significant advantage of composite bonding is the conservation of natural tooth structure. Unlike other restorative procedures, such as dental crowns or veneers, composite bonding requires minimal alteration of the tooth. Only a thin layer of enamel is usually removed during the tooth preparation stage. This conservative approach preserves the integrity of your natural teeth while still delivering remarkable results.
Non-Invasive Procedure
Composite bonding is a non-invasive dental procedure. It eliminates the need for extensive tooth preparation or invasive treatments. The process involves minimal discomfort and does not require significant alterations to your teeth. With composite bonding, you can achieve your desired smile transformation without the anxiety or recovery time associated with more invasive procedures.
Versatility in Addressing Various Dental Issues
Composite bonding is a versatile solution that can address a wide range of dental issues. It is effective in repairing minor chips, closing gaps between teeth, reshaping misaligned teeth, and even lengthening worn-down teeth. The composite material can be molded and sculpted to achieve the desired shape and size, allowing for customized solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Considerations and Limitations
Lifespan of Composite Bonding
Composite bonding is a durable dental solution that can last for several years with proper care. However, it’s important to note that the lifespan of bonded restorations may vary depending on individual factors. On average, composite bonding can last between 5 to 10 years, but it may require touch-ups or replacement over time. Factors such as oral hygiene practices, habits like teeth grinding, and dietary choices can influence the longevity of the bonded restorations.
Potential Risks and Complications
While composite bonding is generally safe, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of. These may include:
Staining: The composite material used in bonding can be prone to staining over time, especially when exposed to certain food and drink substances like coffee, tea, and red wine. Limiting the consumption of staining agents and maintaining good oral hygiene can help prevent or minimize staining.
Chipping or Breakage: Although composite bonding is durable, it can be susceptible to chipping or breakage, particularly if the bonded teeth are subjected to excessive force or trauma. Avoiding habits like biting on hard objects and wearing a mouthguard during physical activities can help protect your bonded teeth.
Decay: While composite material itself is not prone to decay, the natural tooth structure surrounding the bonding can still be susceptible to cavities. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, is essential to prevent decay and maintain the health of your bonded teeth.
Maintenance and Care for Bonded Teeth
Proper maintenance and care are crucial for the longevity and appearance of your bonded teeth. Here are some essential tips:
Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and around the bonded areas.
Avoid Staining Agents: Limit the consumption of foods and beverages that can stain your teeth, such as coffee, tea, and tobacco products. If you do consume these substances, rinse your mouth with water afterward or brush your teeth to minimize staining.
Protect Your Teeth: If you engage in contact sports or grind your teeth, consider wearing a mouthguard or a night guard to protect your bonded teeth from potential damage.
Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to monitor the condition of your bonded teeth and address any potential issues early on.
Conclusion
Composite bonding is a dental procedure that effectively enhances the appearance of teeth through the application of tooth-colored composite resin. This versatile treatment involves the careful placement and sculpting of the resin material onto the teeth, allowing for the correction of various cosmetic concerns such as chipped, discolored, or misaligned teeth. With its minimally invasive nature and ability to blend seamlessly with natural teeth, composite bonding provides patients with a cost-effective and aesthetically pleasing solution. By understanding how does composite bonding works, individuals can confidently explore this transformative dental procedure to achieve a beautiful, confident smile.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does composite bonding work?
Composite bonding involves the application of tooth-colored composite resin to the surface of the teeth, which is then shaped and hardened using a special light, resulting in a natural and seamless appearance.
Is composite bonding a permanent solution?
Composite bonding is a semi-permanent solution as it may require occasional maintenance or repairs over time due to normal wear and tear.
Can composite bonding fix a variety of cosmetic dental issues?
Yes, composite bonding is versatile and can address various cosmetic concerns such as chipped teeth, discoloration, gaps, and minor tooth misalignment, providing a significant improvement in the overall appearance of the smile.