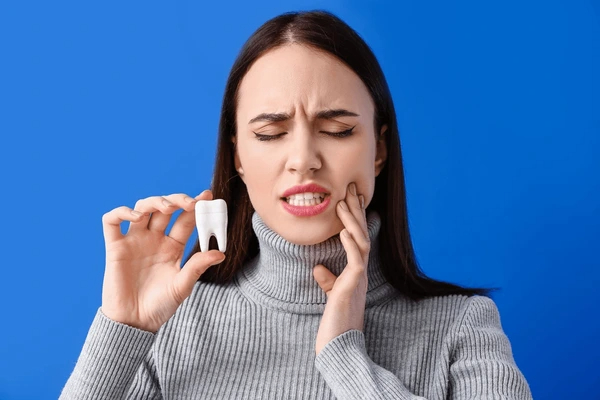
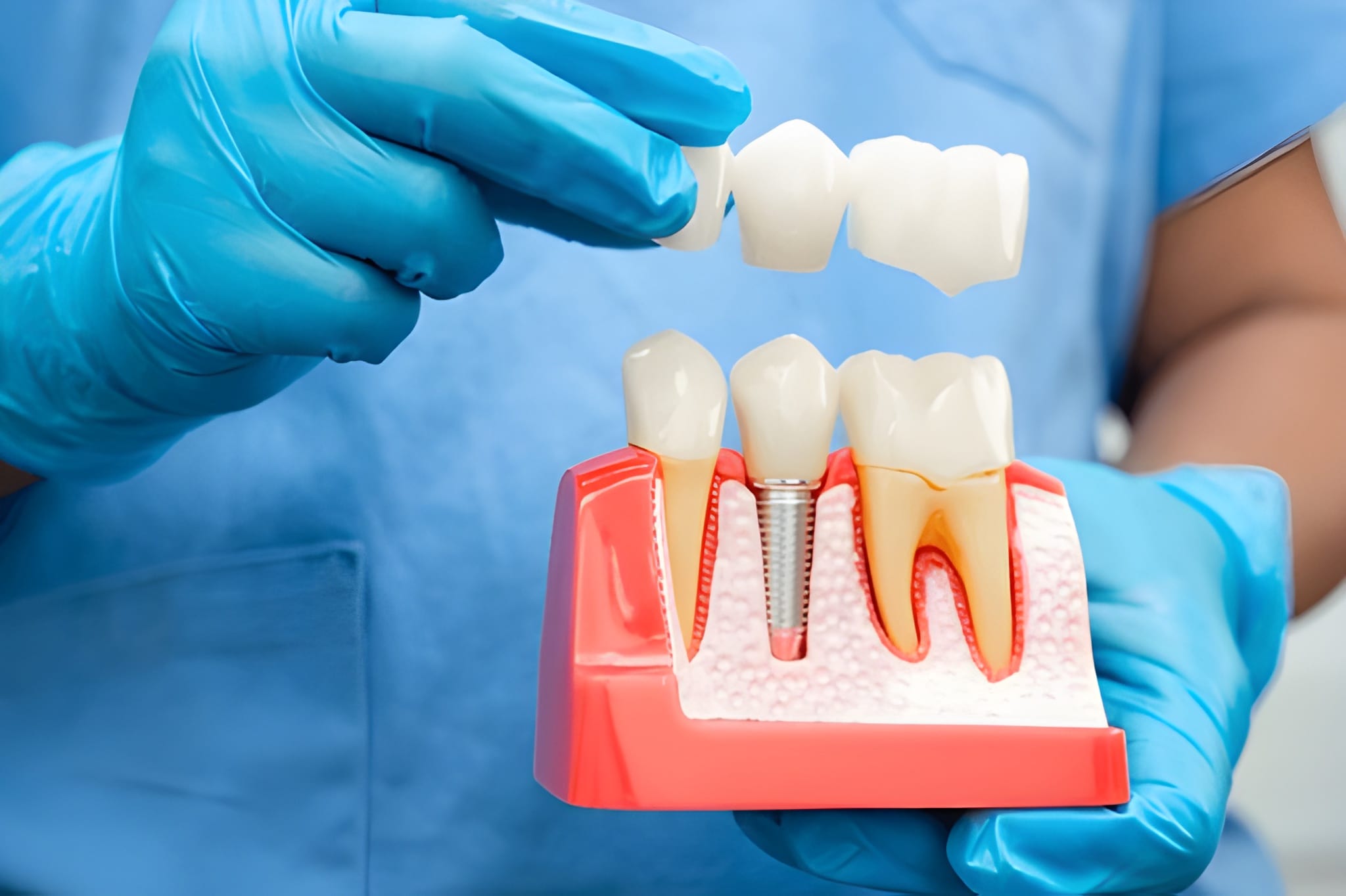
Gum disease is a prevalent but severe oral health disorder that impacts millions of individuals globally. Although most individuals overlook it as a trivial dental problem, the truth is much more shocking. Can gum disease kill you? No, gum disease itself is not an immediate cause of death, but its effect on general health can be lethal. If untreated, gum disease has the potential to lead to serious systemic conditions including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory disease.
In this in-depth guide, we will discuss the relationship between gum disease and overall health, its phases, symptoms, and the most effective treatments that include gum disease receding gums treatment and care prevention strategies. Knowing the risks of gum disease, you can take the actions you need to safeguard your oral and overall health.
Understanding Gum Disease: Symptoms, Stages, and Causes
Gum disease or periodontal disease is an infectious, chronic condition that damages the gums and supporting tissues of the teeth. It may initially manifest as trivial irritation or gum inflammation but eventually progresses to acute conditions that undermine oral health as well as overall health.
This part of the article goes deep into the signs, phases, and causes of gum disease, so that readers can know how to recognize the issue early enough and act before it’s too late.
Early Symptoms of Gum Disease
The initial symptoms of gum disease are normally light, but they are warning signs that a problem exists. Some of the prevailing gum disease signs are:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums – Healthy gums should be firm and pink. If they appear red, puffy, or sore, it may indicate the onset of gum disease. Inflammation occurs as the body’s response to bacterial infection.
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis) – Bacteria trapped in gum pockets release toxins that cause a foul odor. Even after brushing, the bad breath may persist, signaling a problem beneath the gum line.
- Bleeding gums when you brush or floss – Bleeding is one of the first and most frequent signs of gum disease. Healthy gums are not easily bleeding, so if you see blood in your sink when you brush, it may be a sign of gingivitis, the first stage of gum disease.
- Receding gums, which make the teeth look longer – Gum recession is when gum tissues pull back away from the teeth and expose the roots. This makes the teeth sensitive and increases the risk of infection.
- Loose teeth or shifting bite alignment – The supporting structures of the teeth weaken as gum disease advances. This shifts the teeth, makes them loose, or even causes them to fall out in extreme cases.
These symptoms can be slight at first, but if one ignores them, the disease becomes worse over time.
Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease passes through four stages, and each of these stages is more critical if not treated. Identifying the symptoms in each stage helps in taking early treatment.
-
Gingivitis (Early Stage):
- This is the most reversible and mildest type of gum disease.
- Symptoms are red and tender gums, bleeding on brushing, and slight irritation.
- Regular oral hygiene and professional cleanings can reverse gingivitis before it advances.
-
Slight Periodontal Disease:
- Infection begins affecting the deeper structures holding teeth at this stage.
- Symptoms are gum recession, the formation of deeper pockets between gums and teeth, and excess bleeding.
- Although the damage starts at this stage, it may still be controlled through professional care.
Causes of Gum Disease
Knowing the causes of gum disease can prevent it. Some of the top causes of gum disease are:
- Poor Oral Hygiene:
- Poor brushing and flossing let plaque (a sticky layer of bacteria) build up on teeth and gums, causing infection.
- Regular dental cleaning and home care can stop plaque from building up.
- Smoking & Tobacco Use:
- Smoking damages the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to resist gum infections.
- Tobacco smokers have a much greater chance of getting serious periodontal disease.
- Hormonal Shifts:
- Changes in pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can cause gums to become more sensitive and susceptible to infection.
- Pregnant women with periodontal disease are more likely to have premature birth and low birth weight infants.
- Diabetes:
- High levels of blood sugar provide an environment where bacteria can grow strongly, making the gums more susceptible to infection.
- Diabetes and gum disease are a two-way street, i.e., one can aggravate the other.
- Genetic Factors:
- Certain people are genetically predisposed to gum disease despite proper oral hygiene.
- Family history is involved, so those who are genetically predisposed need to be more careful.
- Medications:
- Certain medications, including antidepressants, antihypertensives, and oral contraceptives, can influence saliva production and gum health.
- Decreased saliva flow enhances plaque formation, leading to gum disease.
By treating these risk factors, people can greatly reduce their risk of developing gum disease and have healthier mouths.
These stages of gum disease explain why early treatment is so crucial. The earlier you treat gum disease, the more likely you are to save your natural teeth.
What Causes Gum Disease?
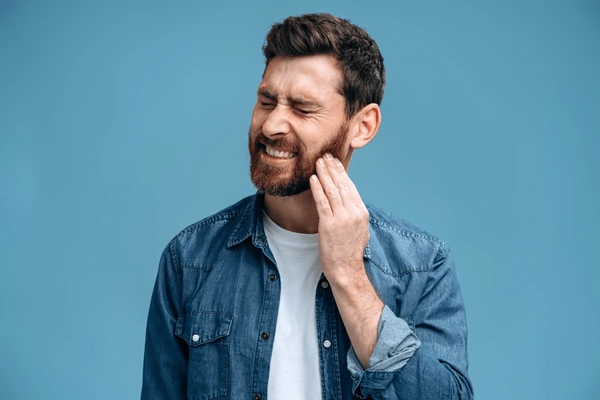

There are a number of factors that cause gum disease, including:
- Poor oral hygiene (brushing and flossing infrequently)
- Smoking and tobacco consumption
- Hormonal fluctuations (pregnancy, menopause)
- Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes
- Some medications that decrease saliva flow
These risk factors may hasten the progression of gum disease. Following good oral hygiene practices and visiting your dentist on a regular basis can prevent gum disease from developing.
Can Gum Disease Be Cured or Reversed?
One of the most asked questions is: Is gum disease curable? The response varies with the stage of the disease. Gingivitis, the initial form, is entirely reversible with good oral hygiene and professional dental care. Advanced periodontal disease, however, needs continuous treatment to control its impact and stop further destruction.
How to Reverse Gum Disease
In time, you can reverse gum disease by:
- Following good oral hygiene, including flossing every day and brushing teeth twice a day.
- Utilizing the best toothpaste for gum disease to stop bacteria growth and harden enamel.
- Utilizing the best mouthwash for gum disease to destroy bacteria and eliminate bad breath.
- Regular dental check-ups and deep cleaning with a dentist.
Once gum disease has progressed or reached the moderate levels, it cannot be reversed but can be controlled by practicing good oral hygiene.
The Connection of Gum Disease with Lethal Diseases
Will Gum Disease Kill You?
Although the gum disease itself is not lethal, it has a very probable chance of developing life-threatening diseases:
- Heart Disease: According to the study, gum disease patients are 19% more likely to develop heart disease.
- Diabetes: It increases blood sugar levels, and therefore diabetes is more difficult to manage.
- Respiratory Diseases: Infections can spread the bacteria from gums to lungs and lead to pneumonia or increase the risk of diseases like COPD.
- Cancer: Individuals with advanced gum disease have a 24% chance of developing certain cancers.
These facts are pointing out that oral health is directly interrelated with general health. Early gum disease treatment can prevent these severe effects.
Successful Gum Disease Treatments: The Best Options
Non-Surgical Gum Disease Treatment
- Scaling and Root Planing: In-depth tooth cleaning below the gumline to remove plaque and bacteria. It is highly successful in the initial stage of gum disease.
- Antibiotics for Gum Disease: Oral or topical antibiotics ease bacterial infection and inflammation elimination.
- Gum Disease Mouthwash: Use of top gum disease mouth rinse wipes away plaque and bacteria control.
Surgical Treatment of Advanced Periodontal Disease
- Flap Surgery: Gum exposure for the removal of deep pockets and reduction in inflammation to prevent further bone loss.
- Gum and Bone Grafts: Restoration of missing bone and structure of tissues to hold up teeth and gums.
- Laser Therapy: A minimally invasive therapy that kills and removes infected tissue without surgery.
These treatments can salvage teeth and restore oral health in people with severe gum disease.
Best Gum Disease Prevention Oral Care Products
In order to maintain the best oral health, a person must use quality oral products. Some of the best rated products are shown below:
Best Toothpaste for Gum Disease
Use fluoride or antibacterial toothpaste specifically formulated to combat plaque and gingivitis. An effective gum disease toothpaste prevents bacterial accumulation and strengthens gum tissue.
Best Mouthwash for Gum Disease
Select an effective gum disease mouthwash containing chlorhexidine or essential oils to destroy bacteria and keep gums healthy.
Best Toothbrush for Gum Disease
A soft-bristled electric toothbrush will softly brush off plaque without bothering sensitive gums.
How Much Is Periodontitis Treatment?
The cost of periodontal disease treatment varies with severity and treatment required:
- Scaling and Root Planing: $200 – $600 per visit
- Surgical Procedures: $500 – $10,000+ (based on complexity)
- Routine Dental Check-ups: $50 – $200 per visit
Preventative care and early intervention can pay you twice over and save you money and your mouth in the long term.
Conclusion
Now that we have given the answer to whether gum disease can kill you, no question is left that such illness is never to be underestimated. Whether the capability to disperse systemic diseases or tooth loss is exhibited or not, such illness needs speedy priority and complete attention.
Dental Scotland: Your Oral Health Partner
Here at Dental Scotland, we provide gum disease treatment for receding gums, Invisalign, dental implants, and composite bonding to get your smile back. Our fully qualified staff offer NHS and private treatment to ensure you receive the treatment you deserve.
Take control of your oral health now—book an appointment with Dental Scotland and retain your smile in the long term!