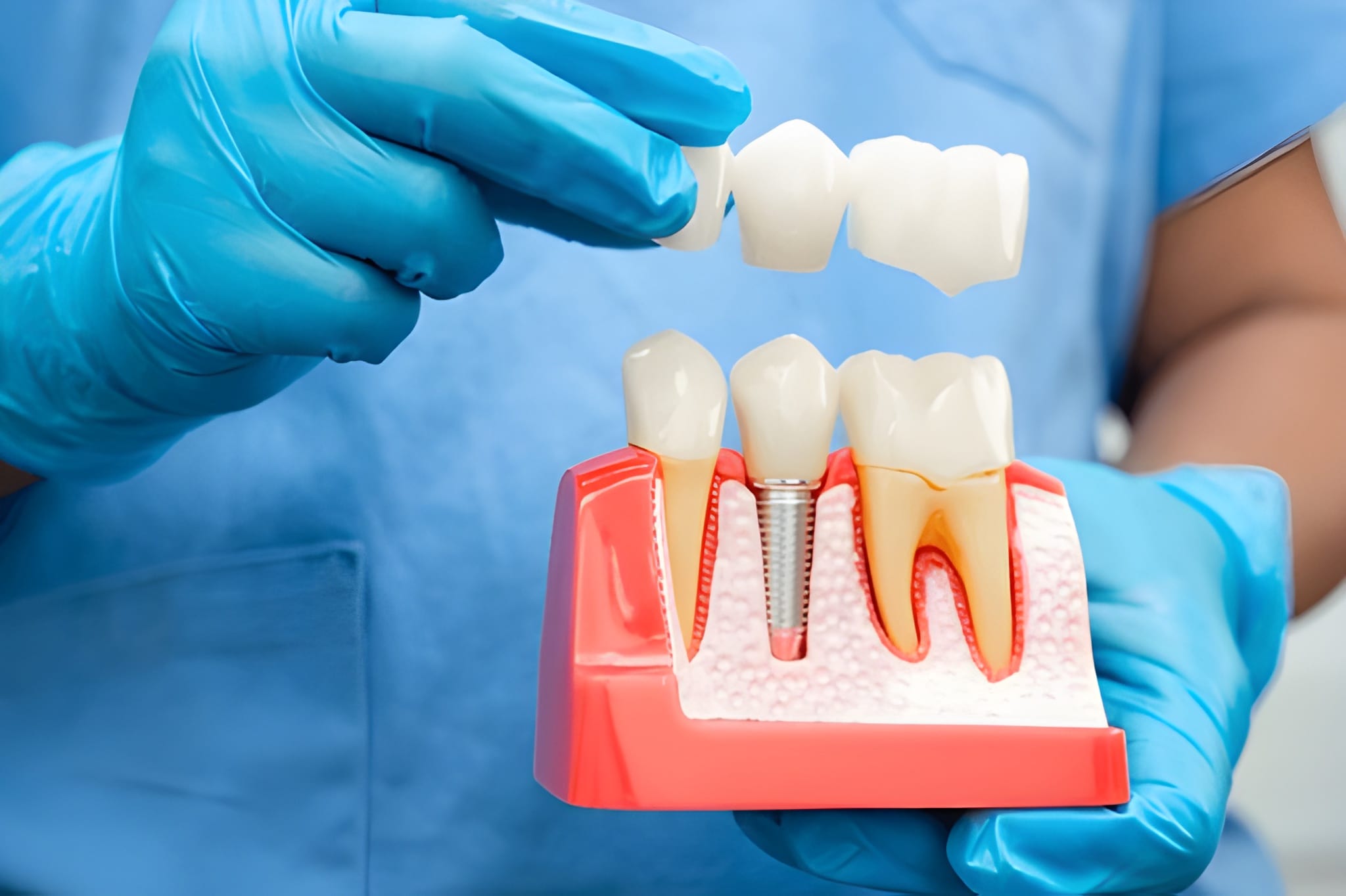
Dental implants are a game-changer for anyone who’s lost a tooth. They bring back not just your smile but also your confidence. But, like anything else, they come with their own set of potential issues. One of the biggest concerns is infection around the implant. Let’s dive into everything you need to know about How to Treat Infection Around Dental Implant?
Understanding Dental Implant Infections
What is Peri-Implantitis?
Peri-implantitis is a type of infection that occurs around dental implants. It is a form of gum disease similar to periodontitis, affecting the tissues surrounding a dental implant. This condition leads to inflammation of the gum and bone loss around the implant. Unlike natural teeth, dental implants lack the periodontal ligament, making infections around them potentially more severe and harder to treat. If left unchecked, peri-implantitis can result in the failure of the dental implant, necessitating its removal.
Causes of Dental Implant Infections
Several factors can contribute to infections around dental implants, including:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque and bacteria around the implant, causing infection.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can impair healing and increase the risk of infection.
- Pre-existing Gum Disease: If you had gum disease before getting an implant, you are at a higher risk of developing an infection around the implant.
- Improper Implant Placement: Incorrect placement of the implant can lead to poor alignment, making it difficult to clean and increasing infection risk.
- Systemic Conditions: Conditions like diabetes can compromise your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections.
- Mechanical Factors: Overloading the implant with excessive force from biting or grinding can damage the surrounding tissues and increase the likelihood of infection.
Diagnosing Dental Implant Infections
Dental Examination
Diagnosing a dental implant infection begins with a thorough dental examination. Your dentist will carefully inspect the area around the implant for signs of inflammation, redness, and bleeding. They will also check for any signs of pus or unusual discharge. During the examination, your dentist will assess the depth of the pockets around the implant using a periodontal probe. Increased pocket depth can indicate peri-implantitis.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques are crucial for a definitive diagnosis of dental implant infections. The most common methods include:
- X-rays: X-rays help in visualizing the bone structure around the implant. They can reveal bone loss, which is a key indicator of peri-implantitis.
- Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT): CBCT scans provide a detailed 3D image of the implant and surrounding tissues. This technique offers a more comprehensive view than traditional X-rays and is particularly useful for assessing the extent of bone loss.
- Periapical Radiographs: These are close-up X-rays of the implant area, helping to identify any small changes in the bone or tissue structure that might not be visible in a broader X-ray.
These imaging techniques allow your dentist to accurately diagnose the severity of the infection and plan an effective treatment strategy.
Preventive Measures
Importance of Oral Hygiene
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is paramount in preventing infections around dental implants. Here are some key practices:
- Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to clean around the implant thoroughly.
- Flossing: Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and around the implant. Special interdental brushes can be useful for cleaning hard-to-reach areas.
- Mouthwash: Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and keep your mouth clean.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential for the early detection and prevention of implant infections. During these visits, your dentist will:
- Professional Cleaning: A professional cleaning removes plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing might miss.
- Examination: Your dentist will examine your gums and implant for any signs of infection or other issues.
- Monitoring: Regular visits allow your dentist to monitor the health of your implant over time and catch any potential problems early.
How to Treat Infection Around Dental Implant?
When to Contact Your Dentist
If you suspect an infection around your dental implant, it’s crucial to contact your dentist immediately. Do not wait for your next scheduled appointment. Here are some signs that indicate you should contact your dentist right away:
- Persistent Pain: Ongoing discomfort or pain around the implant site.
- Swelling and Redness: Noticeable swelling, redness, or inflammation of the gums.
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed easily when touched or brushed.
- Pus or Discharge: Any pus or unusual discharge around the implant.
- Implant Mobility: If the implant feels loose or unstable.
Home Care Tips
While waiting to see your dentist, there are some home care steps you can take to manage the symptoms and potentially slow the progression of the infection:
- Rinse with Salt Water: Use a warm saltwater rinse to help reduce bacteria and soothe the affected area. Mix 1 teaspoon of salt with 8 ounces of warm water and rinse your mouth gently.
- Maintain Oral Hygiene: Continue to brush and floss gently around the implant area to keep it clean. Be careful not to irritate the inflamed tissues.
- Avoid Irritants: Refrain from smoking, as it can worsen the infection and slow down healing. Avoid alcohol and very hot or spicy foods, which can irritate the gums.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Professional Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatments
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are often prescribed to combat bacterial infections around dental implants. These medications help reduce the bacterial load and control the infection. Your dentist will choose the most appropriate antibiotic based on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Cleaning and Scaling
Deep cleaning and scaling procedures are performed to remove plaque and tartar from around the implant. This process includes using specialized instruments to clean the implant surface and surrounding gum tissue. Removing these deposits can help reduce inflammation and allow the tissues to heal.
Surgical Treatments
Flap Surgery
Flap surgery involves lifting the gum tissue to access the implant and surrounding bone more effectively. The dentist will clean the infected area thoroughly and remove any inflamed tissue. This procedure allows for better cleaning and can help control the infection more effectively.
Bone Grafting
In cases where the infection has caused significant bone loss, a bone graft may be necessary. This procedure involves placing bone graft material around the implant to regenerate lost bone and provide better support for the implant. Bone grafting can help stabilize the implant and promote long-term success.
Antibiotics in Treating Dental Implant Infections
Types of Antibiotics
Several types of antibiotics may be used to treat dental implant infections. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include:
- Amoxicillin: A broad-spectrum antibiotic effective against many bacteria commonly found in dental infections.
- Metronidazole: Often used in combination with other antibiotics to target specific bacteria.
- Clindamycin: An alternative for patients allergic to penicillin, effective against a range of oral bacteria.
How They Work
Antibiotics work by targeting the bacteria causing the infection. They can either kill the bacteria (bactericidal) or inhibit their growth (bacteriostatic). By reducing the bacterial load, antibiotics help control the infection and allow the body’s immune system to heal the affected tissues. It’s important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Saltwater Rinse
A saltwater rinse is a simple and effective home remedy for managing mild infections around dental implants. Saltwater has natural antiseptic properties that help reduce bacteria and promote healing. Here’s how to make and use a saltwater rinse:
- Preparation: Mix 1 teaspoon of salt in 8 ounces of warm water.
- Rinsing: Swish the solution around your mouth for about 30 seconds, focusing on the area around the implant.
- Frequency: Use this rinse 2-3 times a day, especially after meals, to keep the area clean and reduce inflammation.
Essential Oils
Certain essential oils have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help manage dental implant infections. Some of the most effective oils include:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its strong antibacterial properties. Dilute a few drops in water and use it as a mouth rinse or add it to your toothpaste.
- Clove Oil: Contains eugenol, which has pain-relieving and antibacterial effects. Apply a small amount directly to the affected area using a cotton swab.
- Peppermint Oil: Its antibacterial properties can help reduce bacteria in the mouth. Add a drop to your toothbrush or use it in a diluted mouth rinse.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Infections
Diet and Nutrition
A healthy diet is crucial for maintaining overall oral health and preventing infections around dental implants. Here are some dietary tips:
- Increase Vitamin C Intake: Vitamin C is essential for gum health and can help prevent infections. Include fruits like oranges, strawberries, and kiwis in your diet.
- Eat Calcium-Rich Foods: Calcium supports strong bones and teeth. Dairy products, leafy greens, and almonds are good sources.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep your mouth clean by washing away food particles and bacteria.
Avoiding Tobacco
Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for infections and complications with dental implants. Smoking can impair healing, reduce blood flow to the gums, and increase the likelihood of infection. Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products can greatly improve your oral health and the longevity of your dental implants. Here are some tips to help you quit:
- Seek Support: Join a support group or seek advice from your healthcare provider.
- Use Nicotine Replacements: Nicotine patches, gums, or lozenges can help manage withdrawal symptoms.
- Stay Active: Physical activity can reduce cravings and improve your overall well-being.
Conclusion
Dental implant infections can be a serious issue if not addressed promptly. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for maintaining the health and longevity of your dental implants. Early diagnosis and intervention, along with good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups, are key to preventing and managing infections around dental implants. By following preventive measures and seeking timely professional care, you can ensure the success of your dental implants and enjoy a healthy smile for years to come.
FAQs
What are the first signs of an infected dental implant?
The first signs of an infected dental implant often include redness and swelling around the implant, bleeding gums, discomfort or pain, and persistent bad breath.
Can a dental implant infection be treated at home?
While home remedies like saltwater rinses and essential oils can help manage minor symptoms, they are not a substitute for professional treatment.
How long does it take for a dental implant infection to heal?
The healing time for a dental implant infection varies depending on the severity of the infection and the treatment method used. Non-surgical treatments like antibiotics and deep cleaning may take a few weeks to show improvement, while surgical treatments like flap surgery or bone grafting may require a longer recovery period.